√1000以上 sinus tachycardia vs ventricular tachycardia 164977-Sinus tachycardia vs supraventricular tachycardia
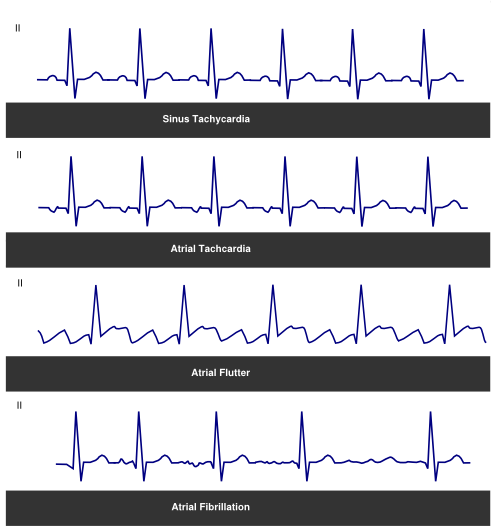
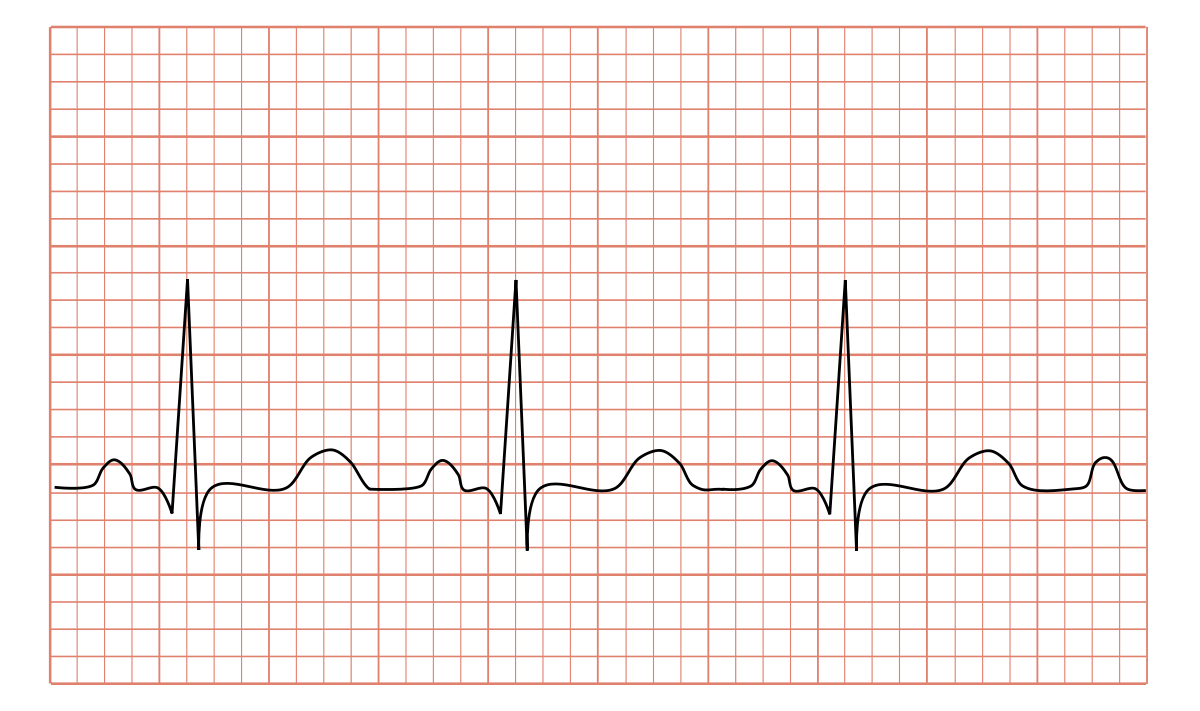
Yesterday, I had encountered a tachycardic patient with heart rate 160/min Somewhere in medical school, I was taught that the sinus tachycardia with heart rate >160/min must be considered as a Supraventricular tachycardia (SVT) With such misinformation, it was easier for me to overlook the fact that the patient was febrile and anemic and even the P wavesSVT is always more symptomatic than sinus tach Sinus tachycardia has a rate of 100 to 150 beats per minute and SVT has a rate of 151 to 250 beats per minute With sinus tach, the P waves and TSinus tachycardia vs Sinus bradycardia vs Sinus arrhythmia A) Sinus tachycardia is sinus rhythm with heart rate over 100/min This rhythm is regular with normal appearance P wave and normal duration PR intervals QRS complexes can be narrow or wide B) Sinus bradycardia is sinus rhythm with heart rate bellow 60/min

Ventricular Tachycardia Electrocardiography Sinus Tachycardia Heart Heart Angle Text Rectangle Png Pngwing
Sinus tachycardia vs supraventricular tachycardia
Sinus tachycardia vs supraventricular tachycardia-If adenosine fails, initiate rate control with calcium channel blocker or beta blocker or use synchronized cardioversionVentricular tachycardia (VT or Vtach) is a potentially lifethreatening cardiac arrhythmia that originates in the ventricles It is usually a regular, wide complex tachycardia with a rate between 1 and 250 beats per minute A medically significant subvariant of Ventricular Tachycardia is called Torsades de Pointes (literally meaning Twisting of the Points due to its appearance on an




Ventricular Tachycardia Hd Stock Images Shutterstock
Atrial tachycardia is a least common type of supraventricular tachycardia (SVT), constituting 515% of all SVTs, that does not require the atrioventricular (AV) junction, accessory pathways, or ventricular tissue for its initiation and maintenance Atrial tachycardia may occur at any age, although it is more common in children and adults with congenital heart disease Atrial tachycardiaSinus tachycardia is recognized on an ECG with a normal upright P wave in lead II preceding every QRS complex, indicating that the pacemaker is coming from the sinusSupraventricular tachycardia (SVT) is a common nonarrest dysrhythmia seen in children,especially during infancy, and is the main cause of cardiac related instability Most infants with SVT will outgrow the syndrome without lasting effects History of the complaint is the key to proper distinction between SVT and rapid sinus tachycardia
Atria just forces extra 25% of blood to the ventricles during diastole It also happens that the SA node, as the name implies, is located in atria I find that sometimes we are confused by all these terms Tachycardia, Ventricular tachycardia, Supra ventricular tachycardia, Sinus tachycardia etcAtrial and ventricular signals were recorded during sinus rhythm,atrial flutter,atrial fibrillation and ventricular tachycardia or ventricular fibrillation bnkde Atr ia le a nd ventrikuläre Si gnale wu rden während Sinusrhythmus,Vorhofflattern,Vorhofflimmern sowie während Kammertachykardi en und Kammerflimmern aufg ez eichnet100 bpm • As rate increases, amplitude of P wave will increases due to enhanced activation of the sinus node and associated atrial depolarization • ST is caused by enhanced sympathetic activity in both physiologic (eg exercise, stress) and pathologic (e
On occasion the sinus rate can be different than the ventricular rate (AV dissociation) such as in ventricular tachycardia or complete heart block Treatment is aimed at the primary cause ThePremature Ventricular Contractions (PVCs) are single beats originating from the lower chambers Any time there is more than 3 beats in succession this is defined as ventricular tachycardia Most of the time ventricular tachycardia occurs in people with underlying heart abnormalities Sometimes in can occur in structurally normal hearts In these patients the origin is usually the right ventricular2402Catecholaminergic polymorphic ventricular tachycardia (CPVT) is a rare genetic arrhythmia syndrome characterized by polymorphic ventricular tachycardia (VT) during exercise or stress in young patients with structurally normal hearts 1 The diagnosis is often made during exercise treadmill testing, with a typical reproducible progression from sinus rhythm to isolated premature ventricular
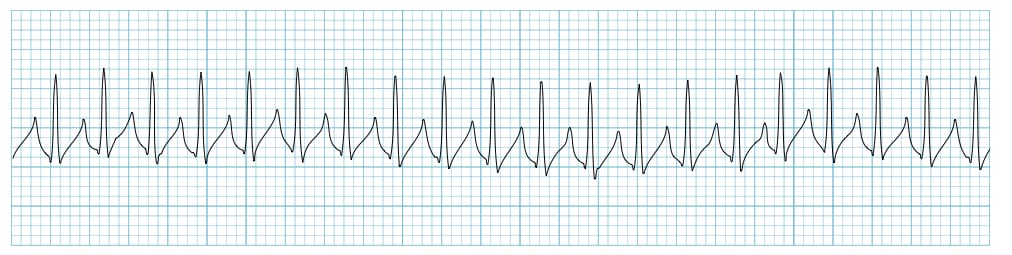



Supraventricular Tachycardia Svt Litfl Ecg Library Diagnosis




Arrhythmias Presentation And Associated Disease Matt Wright What
100 bpm, with narrow QRS complexes but Pwaves that do not originate from the sinus node but from another site in the atria A heart rate that is greater than 100 beats per minute in an adult is identified as tachycardia Sinus tachycardiaSINUS TACHYCARDIA • Sinus tachycardia (ST) is sinus rhythm with fast heart rate >Narrow complex tachycardia (QRS<1ms) indicates normal ventricular conduction and therefore a supraventricular source of arrhythmia As with sinus rhythm, leads V1 and II are helpful to identify flutter waves, which most commonly proceed in a counterclockwise loop away from lead II (producing inverted flutter waves) and towards V1 (producing upright flutter waves mimicking P waves) Wide complex tachycardia




The Ekg Guy Rhythm Challenge Learn How To Differentiate
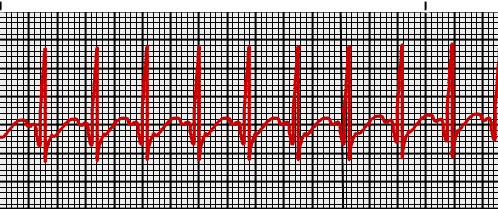



Supraventricular Tachycardia Vs Sinus Tachycardia Epomedicine
0118Sinus tachycardia refers to a fasterthanusual heart rhythm Your heart has a natural pacemaker called the sinus node, which generates electrical• When the sinus beat is conducted at the same time as the ventricular beat, • RBBBlike QRS's are often >In this video flight paramedic and instructor Ryan Wyatt discusses how to identify the difference between SVT and sinus tachycardia This is part two of thre
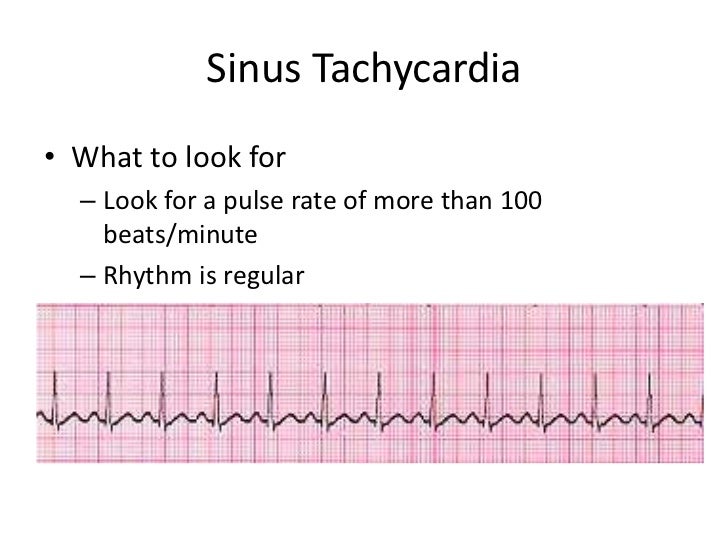



Sinus Tachycardia




Ecg Sinus Tachycardia Youtube
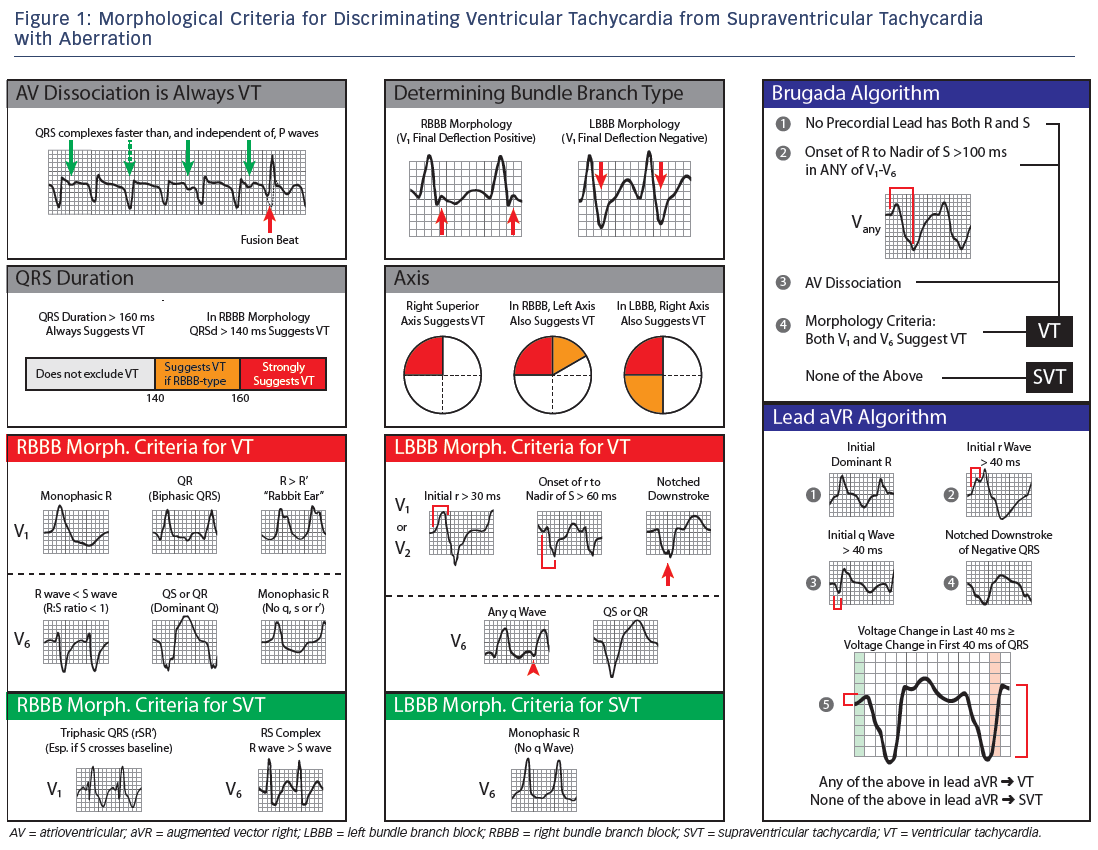
Fig 404 Capture and fusion beats in ventricular tachycardia (VT) Sinus rhythm giving way to a broad complex tachycardia P waves are arrowed, bold ones = P waves visible on the ECG, lighter arrows P waves 'swallowed' by the QRS complex P waves are most easily visible on the top or bottom of a QRS complexDr David Krulak answered 23 years experience Family Medicine Yes Generally speaking, it should not be too difficult for your doctor to differentiate between the two on your EKG 0 0 comment 1 1 thank Send thanks to the doctor 90,000 USSVT Vagal maneuvers (convert up to 25%) Adenosine 6mg rapid IV push if patient hemodynamically stable (unstable should proceed directly to electrical cardioversion) Can follow with repeat dose of 6 mg or 12mg if initially fails;




Intro To Ekg Interpretation Overview Of Tachyarrhythmias Youtube



1
Supraventricular Tachycardia (SVT) and Atrial Tachycardia (AT) Fast heart rhythms (arrhythmias) that involve the upper chambers of the heart are often referred to as SVTs (supraventricular tachycardias) and can often be treated with an SVT ablation These arrhythmias cause the heart to suddenly beat very quickly due to an electrical 'shortAtrial tachycardia with or without blocks;Sinus tachycardia is when the sinus node in the heart sends electrical impulses faster than the normal rate, resulting in an increased heart rate Learn more in this article
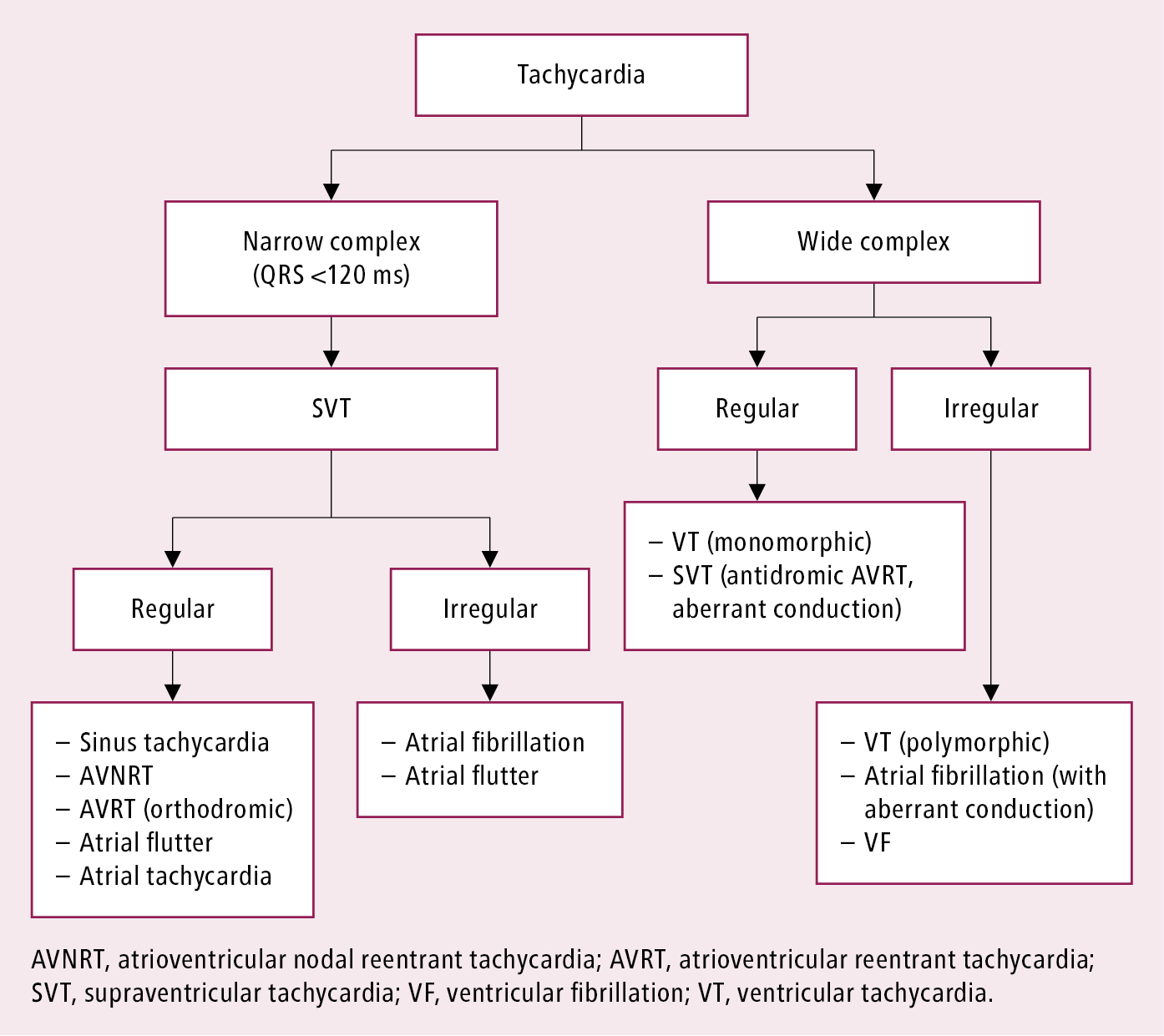



Cardiac Arrhythmias Cardiovascular Diseases Diseases Mcmaster Textbook Of Internal Medicine




8 Ventricular Tachycardia Ideas Ventricular Tachycardia Cardiac Nursing Nursing School Notes
We present the case of a patient who developed newonset asymptomatic sinus tachycardia after undergoing treatment for a right ventricular myocardial infarction Even after excluding heart failure, infection and bleeding, the sinus tachycardia persisted Computed tomography pulmonary angiography shoIn reality, sinus tachycardia is a form of SVT, and the rate can easily exceed 150 A good rule of thumb to estimate the maximum sinus rate is 2 minus age but that can vary by 1015%, which is a lot What most people really mean when they call a rhythm "SVT" is AV Nodal Reentrant Tachycardia or AVNRT, which is a reentrant rhythm in or around the AV node ThisBasis and Goals of Ventricular Tachycardia Criteria In contrast to the SVTs described above, with relatively constrained modes of ventricular activation, VT can originate from literally any location within the ventricular myocardium or its specialised conduction tissues As a result of this, VT can appear identical to any of the wide complex SVTs above and it is nearly impossible to say with absolute certainty, from an ECG of freerunning tachycardia



Sinus Tach Or Svt 4 Clues To Tell The Difference




Supraventricular Tachycardia Wikipedia
Svt vs sinus tachycardia A 19yearold female asked are there any distinct differences between svt and sinus tachycardia on an ecg?160 ms are highly suggestive of ventricular tachycardia vs SVT with aberrancy 7 prolonged rs • Because the impulses from the aberrant ventricular focus rather spread to neighboring ventricular myocardia and not going through the0711SupraVentricular Tachycardia vs Sinus Tachycardia In what looks like it will be the last in this series, for a while, Brandon Oto of EMS Basics wrote this comment to Rhythm Interpretation and Inattentional Blindness We're talking past each other a bit, and I think we're in agreement on most points




Treatment Of Ventricular Arrhythmias The Cardiology Advisor




Ecg Quiz Very Wide And Very Fast Emergency Physicians Monthly
Note that sinus tachycardia may be accompanied by frequent premature atrial beats (atrial ectopic beats), which may give the sinus rhythm an irregular ventricular rhythm that may be confused with atrial fibrillation Also recall inappropriate sinus tachycardia, which is a condition with increased automaticity in the sinoatrial node without any known cause The last tachycardia arising in theUnderstanding Tachycardia Tachycardia can be categorized by the location from which it originates in the heart Two types of tachycardia we commonly treat are Supraventricular tachycardia (SVT) begins in the upper portion of the heart, usually the atria;04Ventricular tachycardia – Often with highseptal origin, which accesses the HisPurkinje system Approach to diagnosis Medical students and PGY12 residents should make the distinction between irregular narrow complex tachycardia and regular narrow complex tachycardia (aka SVT), and should know the differential diagnosis and the initial management




Cardiovascular Medicine Wide Complex Tachycardia




Ventricular Tachycardia Hd Stock Images Shutterstock
Ventricular Tachycardia Ventricular tachycardia is an abnormal ventricular rhythm with a pulse rate above 100 beats per minute Ventricular tachycardia presents with palpitations, chest pain, and difficulty in breathing They may also come in a state of cardiac arrest Electrocardiogram (ECG) shows regular R waves in the absence of atrial rhythm All R waves are similar and regular Ventricular tachycardia0100Focal atrial tachycardia (FAT) is a form of supraventricular tachycardia (SVT) originating from a single ectopic focus within the atria but outside of the sinus node Focal atrial tachycardia (FAT) Consistent, abnormal P wave morphology indicating an ectopic focus The term FAT is commonly used synonymously with atrial tachycardia, a broader0100The term supraventricular tachycardia (SVT) refers to any tachydysrhythmia arising from above the level of the Bundle of His, and encompasses regular atrial, irregular atrial, and regular atrioventricular tachycardias It is often used synonymously with AV nodal reentry tachycardia (AVNRT), a form of SVT In the absence of aberrant conduction (eg



Tachycardia Textbook Of Cardiology



Wide Complex Tachycardia Ventricular Tachycardia Or Not Ventricular Tachycardia That Remains The Question Aer Journal
Bradycardia induced ventricular tachycardia (sinus bradycardia, AVblock etc) Bradycardia may induce premature ventricular complexes and ventricular arrhythmias These are treated with atropine, isoproterenol (isoprenaline) or transvenous pacing Longterm treatment of ventricular tachycardia Patients with preserved left ventricular function and asymptomatic nonsustained ventricularSinus tachycardia in the setting of acute MI usually occurs in response to an increase in sympathetic tone and can be seen in up to 30% of cases 1–2 However, patients with isolated sinus tachycardia during acute MI fare more poorly than those without 8,9 Acutely, MI patients with sinus tachycardia have higher levels of cardiac biomarker release, a larger proportion ofInappropriate sinus tachycardia is a rare type of cardiac arrhythmia within the category of supraventricular tachycardia (SVT) Atrial tachycardia has a more or less regular heart rate >




Automatic Tachycardia Wikipedia



Tachycardia Wikipedia
140 ms and LBBBlike QRS's are often >Ventricular tachycardia is a condition in which the SA node no longer controls the beating of the ventricles Instead, other areas along the lower electrical pathway take over the pacemaking role Since the new signal does not move through your heart muscle along the regular route, the heart muscle does not beat normally Your heartbeat quickens, and you feel as if your heart isVentricular tachycardia (VT) begins in the heart's lower chambers, the ventricles



Catheter Ablation Of An Incessant Ventricular Tachycardia Originating From The Left Aortic Sinus Cusp In An Adolescent With Subacute Myocarditis Springerlink




Ventricular Tachycardia Amboss
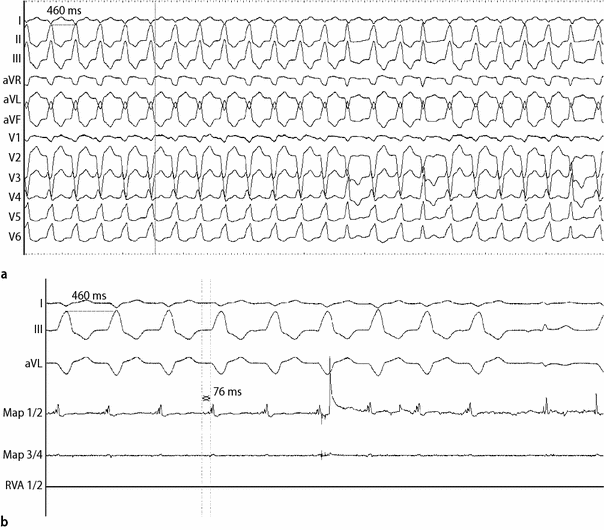
Introduction The voltage map during sinus rhythm (SR) is a cornerstone of substrate mapping (SM) in scarrelated ventricular tachycardia (VT) and frequently used with pace mapping (PM) Where to conduct PM is unclear in cases of an extensive or unidentified substrate Conduction properties are another aspect incorporated by SM, and conduction slowing has gained interest as beingSo where ever you practice , whether in remote Nigerian village or sophisticated Cleveland university hospital , when you are confronted with a tachycardia the diagnosis should be one among the following five !) Sinus tachycardia AF/Afib;If the patient then develops tachycardia in the background of this BBB (eg SVT, sinus tachycardia, etc), this will be seen as a wide complex tachycardia In much the same way, an irregular wide complex tachycardia is almost always from a patient who has a baseline EKG with a wide QRS complex who then develops an irregular tachycardia (eg Afib with RVR, AFlutter
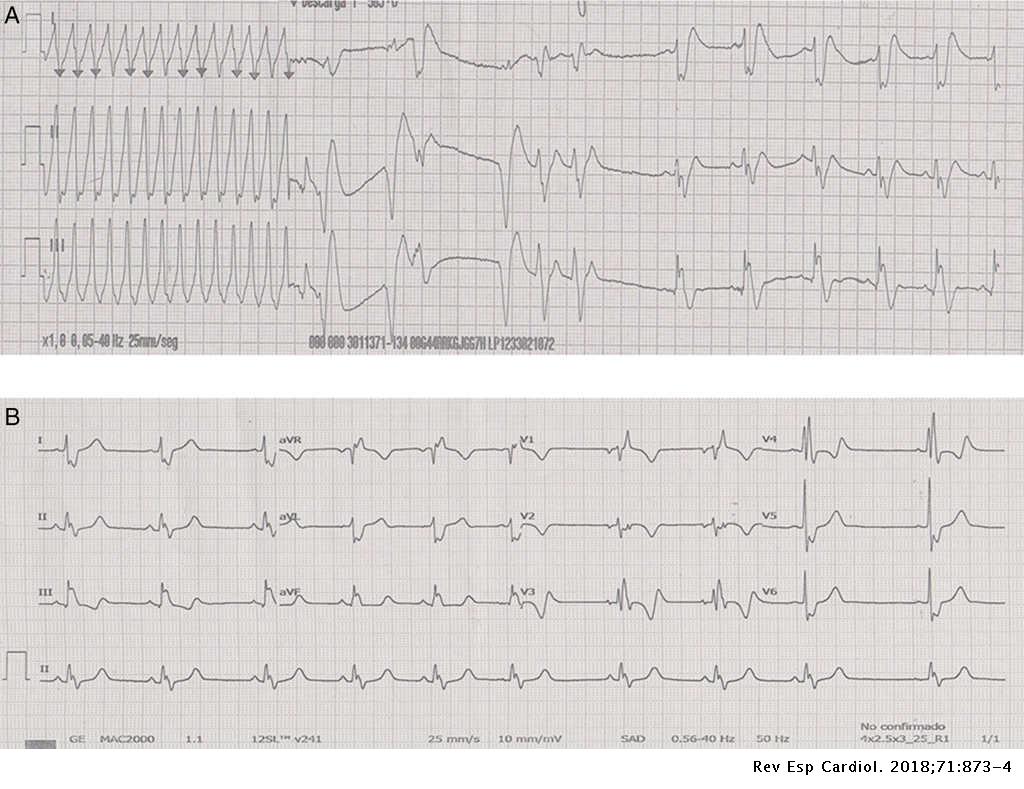



Sustained Ventricular Tachycardia After Thoracic Traumatism In A Patient With Repaired Tetralogy Of Fallot Revista Espanola De Cardiologia



Cardiac Arrhythmia Cardiosecur
Sinus tachycardia Treat underlying cause;Sinus tachycardia can be mistaken for other supraventricular arrhythmias, including atrial flutter, particularly with rapid tachyarrhythmias (when P waves are difficult to distinguish or when ectopic atrial foci originate near the sinoatrial node, such as near the superior vena cava or upper crista terminalis) Atrial versus ventricular arrhythmia Whether the arrhythmia originates#Ventricular #tachycardia and #supraventricular tachycardia with aberrancy how to differentiate




Management Of Tachycardia Amboss
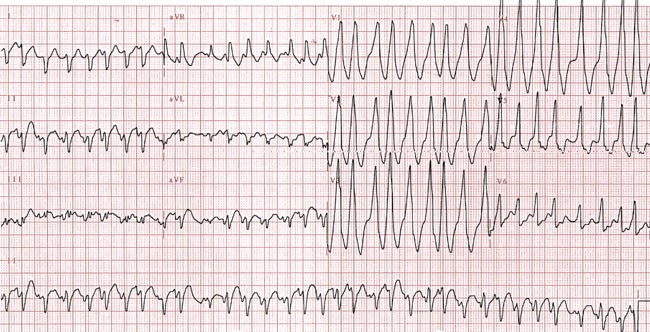



The Diagnosis And Management Of Ventricular Arrhythmias Nature Reviews Cardiology
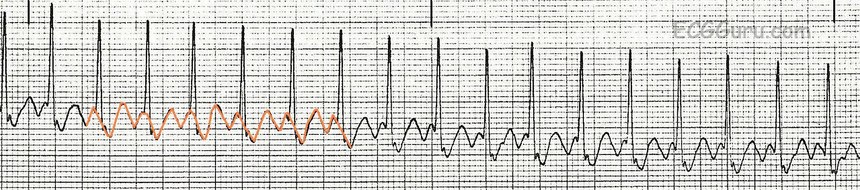
0706At first glance, this tracing suggests rapid polymorphic ventricular tachycardia It is actually sinus rhythm with premature atrial complex and a superimposed lead motion artifact Hidden sinusAny supraventricular tachycardia (SVT), such as atrial flutter, sinus tachycardia, AV nodal reentry tachycardia (AVNRT), or AV reentry tachycardia (AVRT) with aberrancy, is probably the most difficult confounder of a monomorphic ventricular tachycardia when interpreting the ECG of a regular widecomplex tachycardia SVT episodes can occur in anyRhythm analysis indicates sinus tachycardia at over 100 bpm First degree heart block is also present This encounter shows a fast rate over 100 bpm, with a regular rhythm and P waves, indicating sinus tachycardia The extremely long delay between the P wave and QRS indicates first degree heart block Additionally, ectopy is seen in this encounter, in the form of premature ventricular



Mcgill Ekg Learning Project




Sinus Tachycardia Images Stock Photos Vectors Shutterstock
Atrial tachycardia vs sinus tach A flutter vs atrial tachycardia Connect by text or video with a US boardcertified doctor now — wait time is less than 1 minute!1512Normal sinus rhythm presents with the same electrographic features as sinus tachycardia, with the exception that the heart rate is between 60 and 100 beats per minute Supraventricular tachycardias present with a heart rate greater than 100 beats per minute and a narrow QRS (less than 1 milliseconds) 48
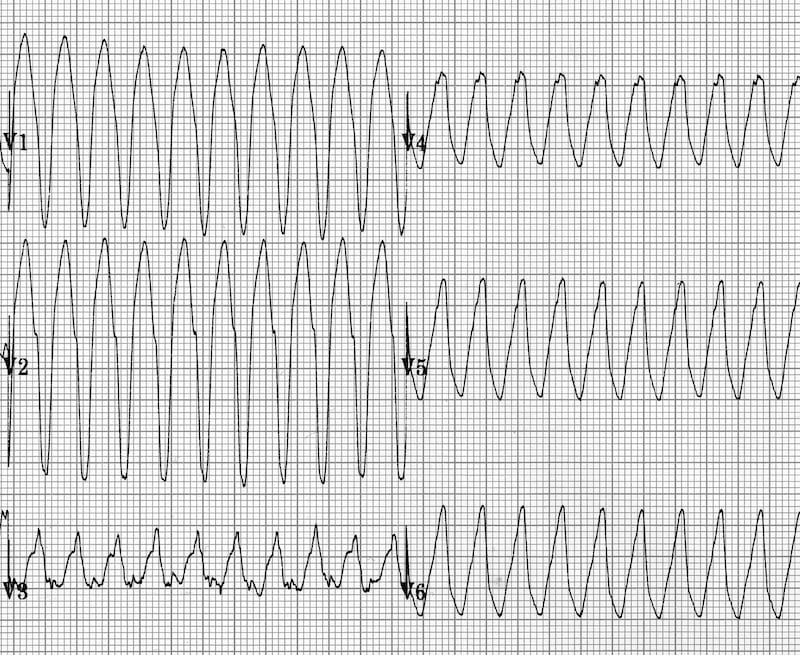



Vt Versus Svt Litfl Medical Blog Ecg Library Basics
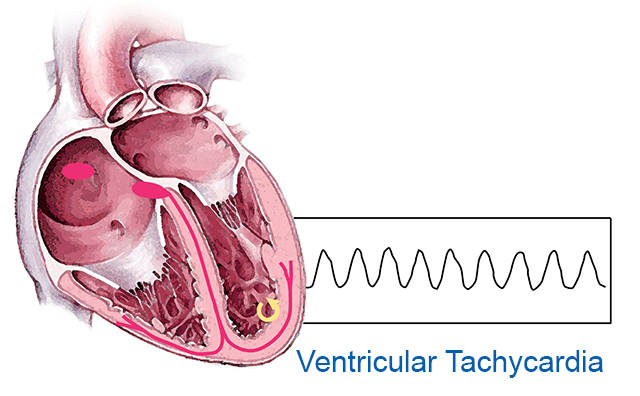



Ventricular Tachycardia Johns Hopkins Medicine
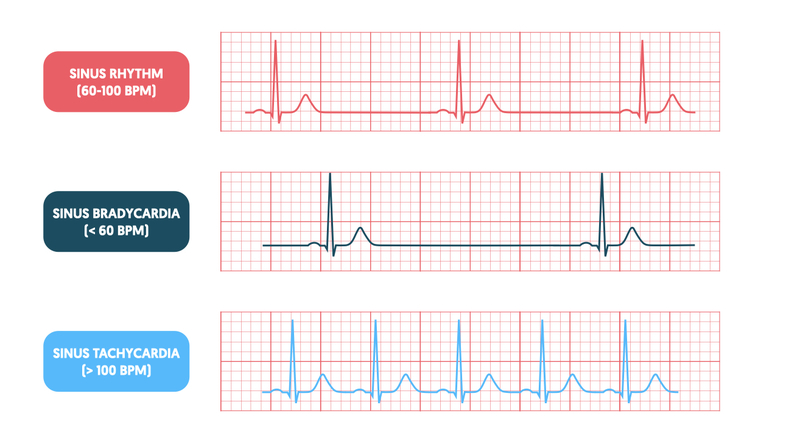



Pulsenotes Tachycardias
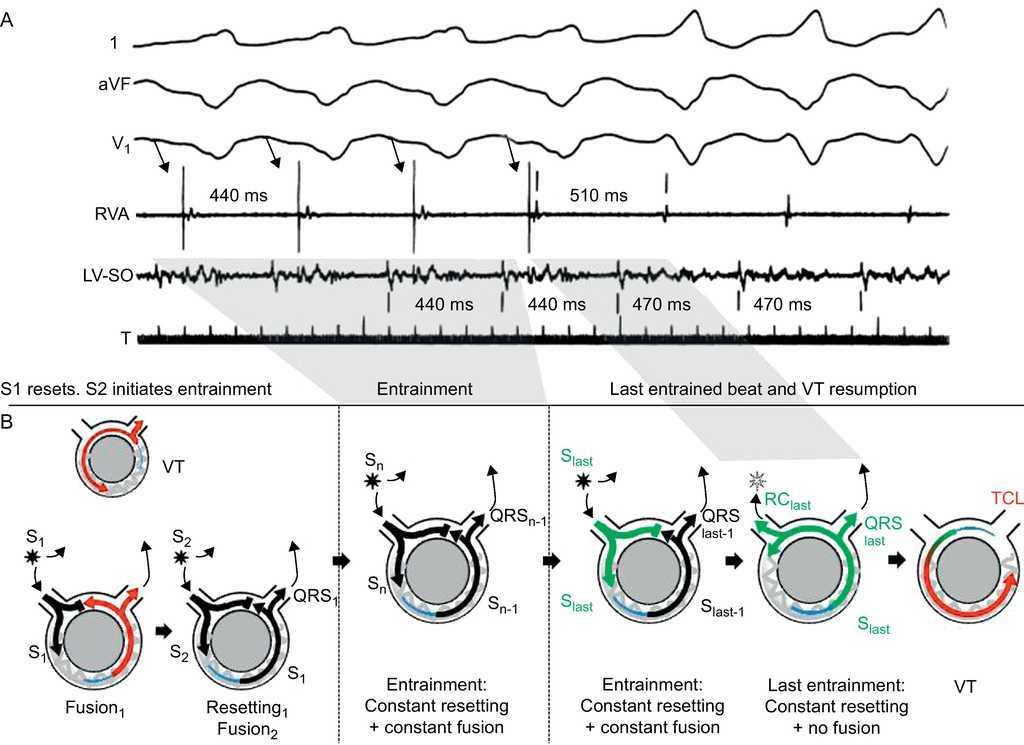



Ventricular Tachycardia In Coronary Artery Disease Revista Espanola De Cardiologia




Pin On Public Health Medicine Nursing Dentistry Case Management Research International Medicine
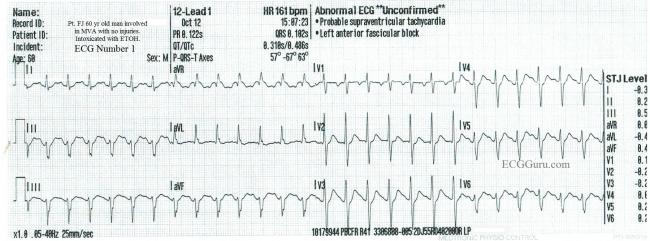



Sinus Tach Vs Svt In An Inebriated Patient Ecg Guru Instructor Resources




Ventricular Tachycardia Electrocardiography Sinus Tachycardia Heart Heart Angle Text Rectangle Png Pngwing
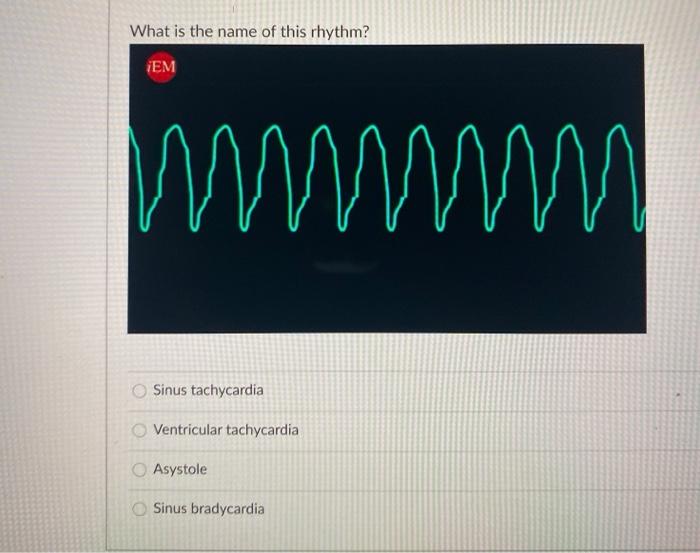



Solved What Is The Name Of This Rhythm Nhunhunhunkumhamh Chegg Com




Sinus Tachycardia A Condition With Faster Than Usual Heart Rhythm Youtube




Arrhythmia Case Studies Prezentaciya Onlajn
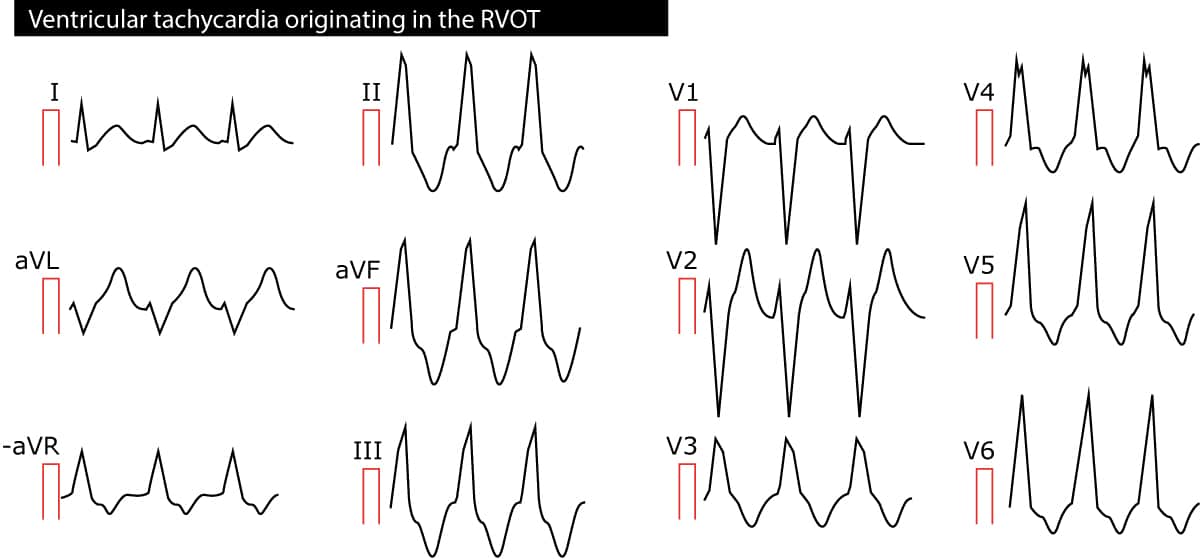



Ventricular Tachycardia Vt Ecg Criteria Causes Classification Treatment Management Ecg Echo




Vt Ventricular Tachycardia Vs Svt Supraventricular Tachycardia With Aberrancy Youtube
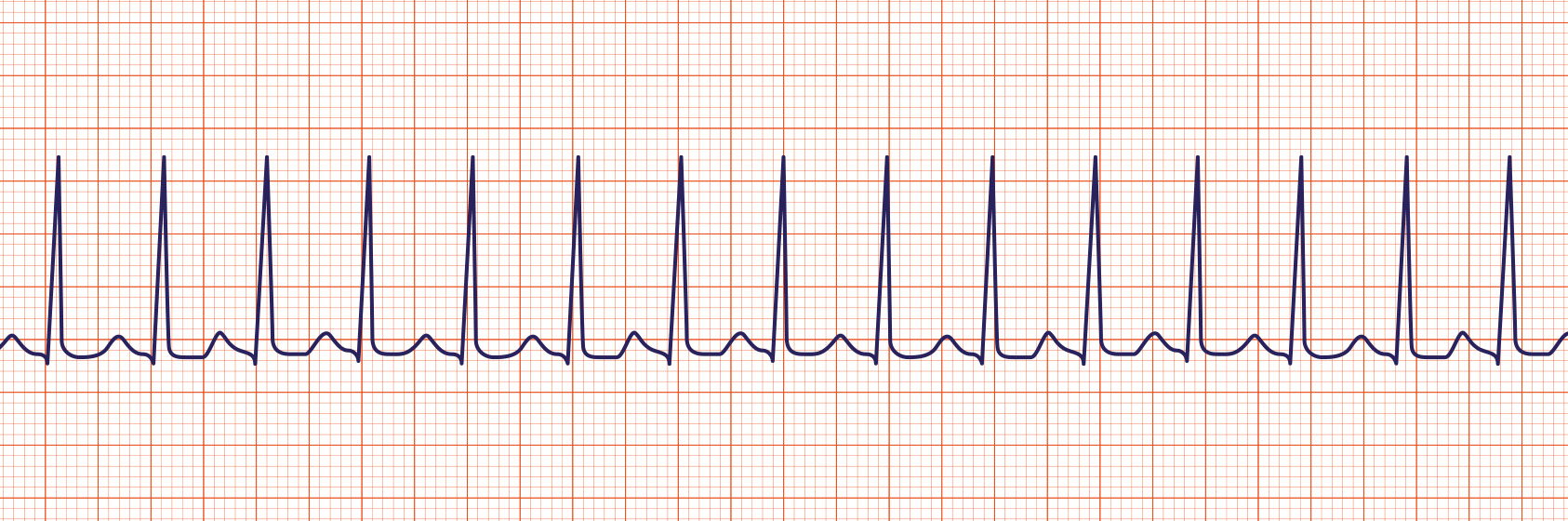



Rhythm Recognition Acls Medical Training




Sinus Tachycardia Wikipedia
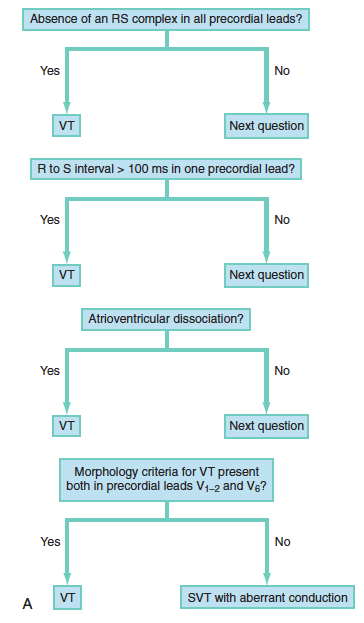



Ventricular Tachycardia Core Em




Catheter Ablation For Ventricular Tachycardia Circulation



1




Supraventricular Arrhythmias Clinical Framework And Common Scenarios For The Internist Mayo Clinic Proceedings




Video Sinus Tachycardia Vs Svt In 60 Seconds The Visual Nurse
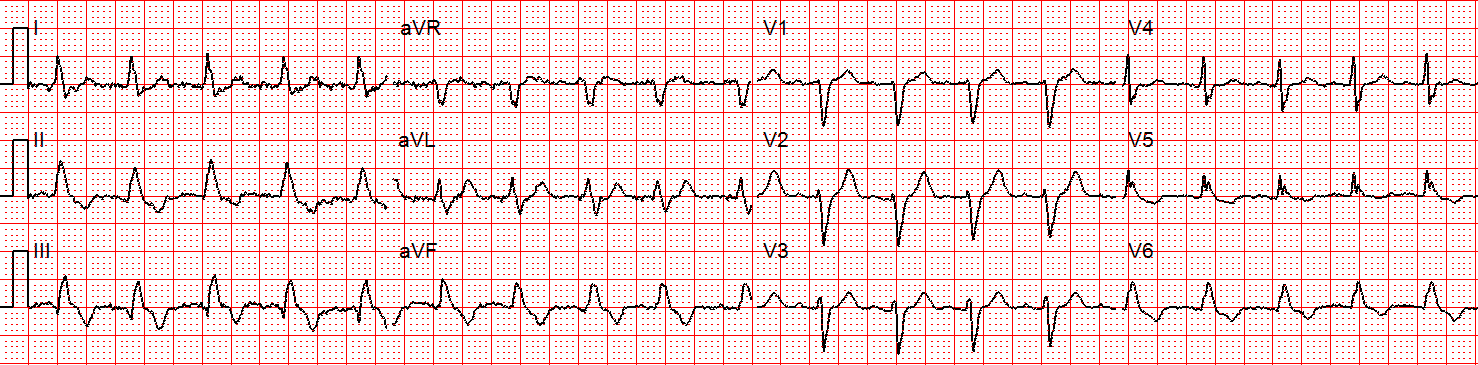



Svt With Aberrancy Or Ventricular Tachycardia Acls Medical Training



Ventricular Tachycardia Vt Types And Ecg Online Medical Library
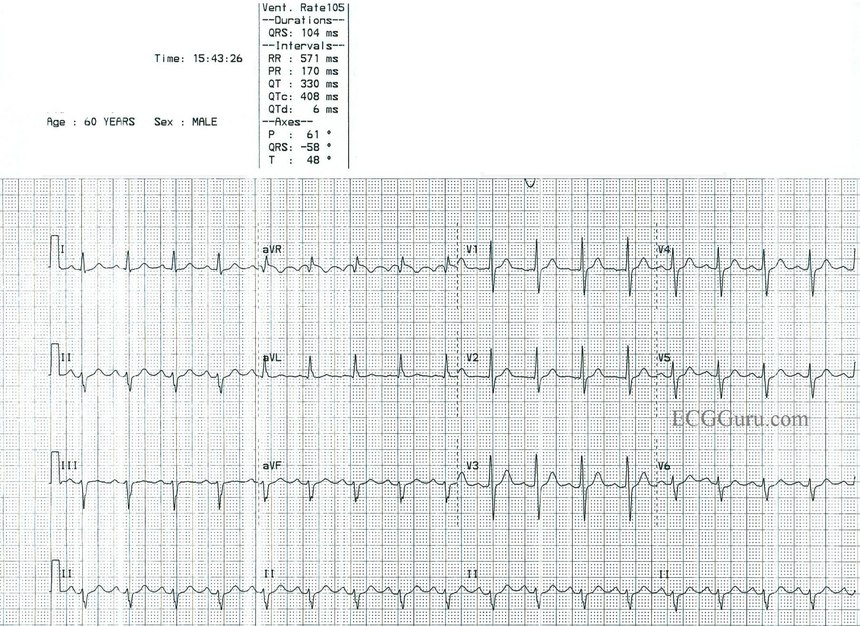



Sinus Tach Or Svt 4 Clues To Tell The Difference
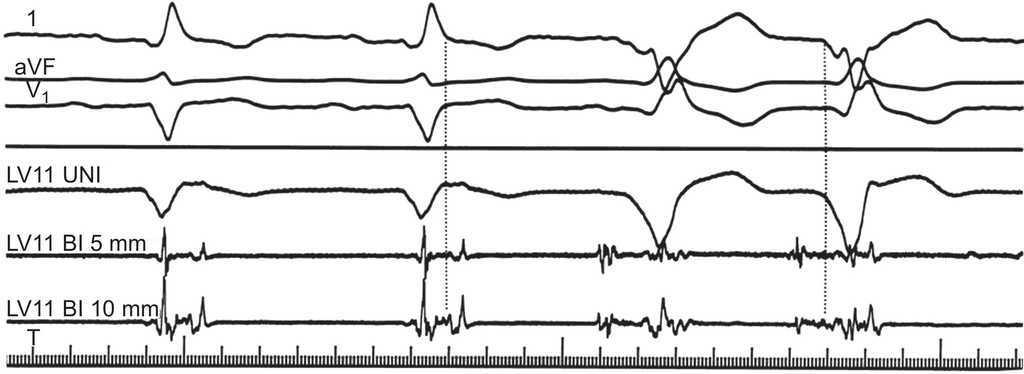



Ventricular Tachycardia In Coronary Artery Disease Revista Espanola De Cardiologia




Ventricular Tachycardia Vt Cardiovascular Disorders Msd Manual Professional Edition




Ecg Shows Uniform Ventricular Tachycardia First 6 Complexes Followed Download Scientific Diagram




Holter Electrocardiogram Revealed A Paroxysmal Sinus Tachycardia During Download Scientific Diagram
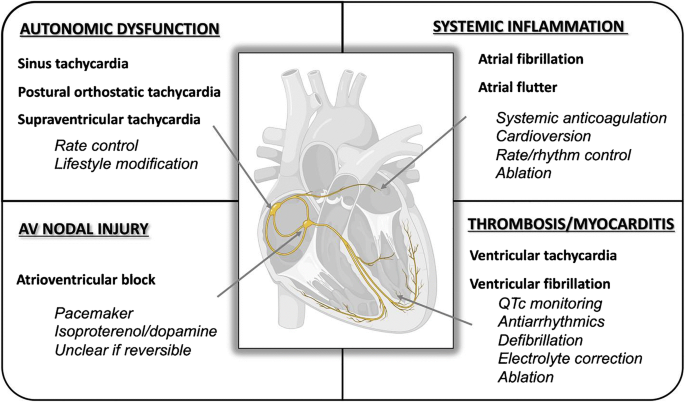



Management Of Arrhythmias Associated With Covid 19 Springerlink




4 Human Ecgs During A Normal Sinus Rhythm Nsr Top B Download Scientific Diagram




Ecg For Acls




Electrocardiogram Showing Sinus Tachycardia And Left Ventricular Download Scientific Diagram
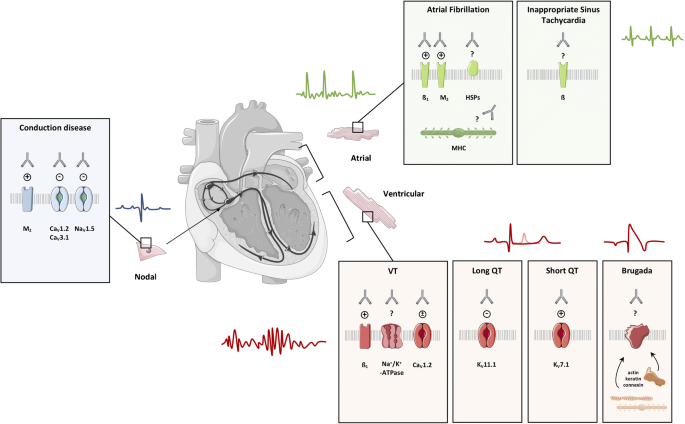



The Role Of Autoantibodies In Arrhythmogenesis Springerlink
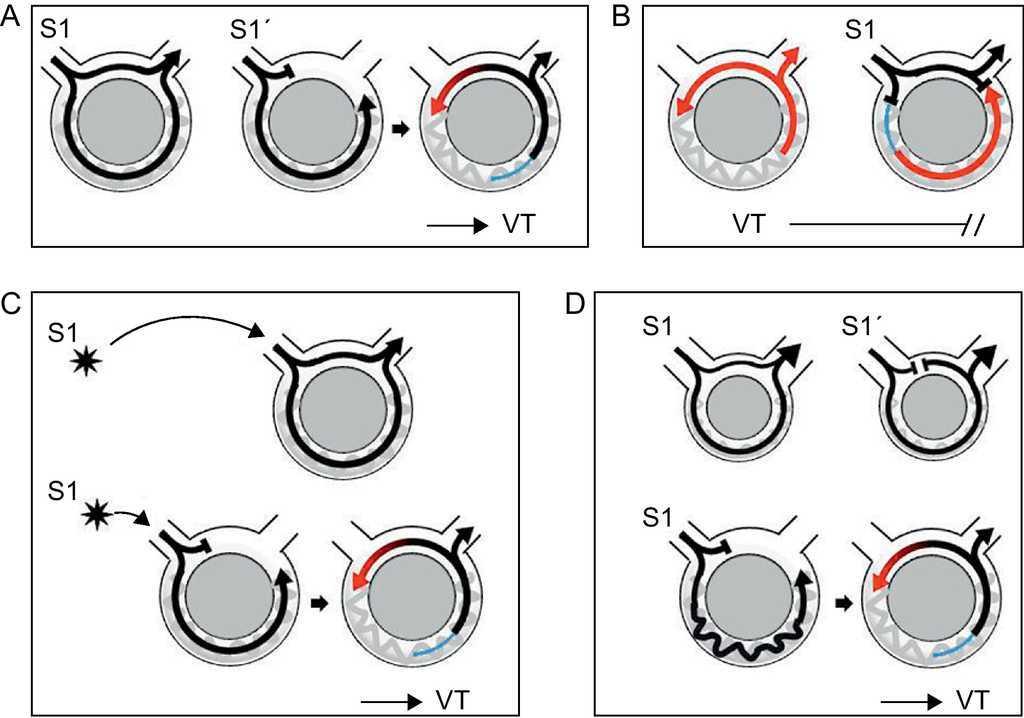



Ventricular Tachycardia In Coronary Artery Disease Revista Espanola De Cardiologia




Smartwatch Detection Of Ventricular Tachycardia Case Series Heartrhythm Case Reports




Infarct Related Ventricular Tachycardia Redefining The Electrophysiological Substrate Of The Isthmus During Sinus Rhythm Jacc Clinical Electrophysiology




Sinus Tachycardia Wikipedia



1



What S The Difference Between Sinus Tachycardia And Svt Quora




Example Of Ventricular Tachycardia In The Context Of Inappropriate Pmt Download Scientific Diagram
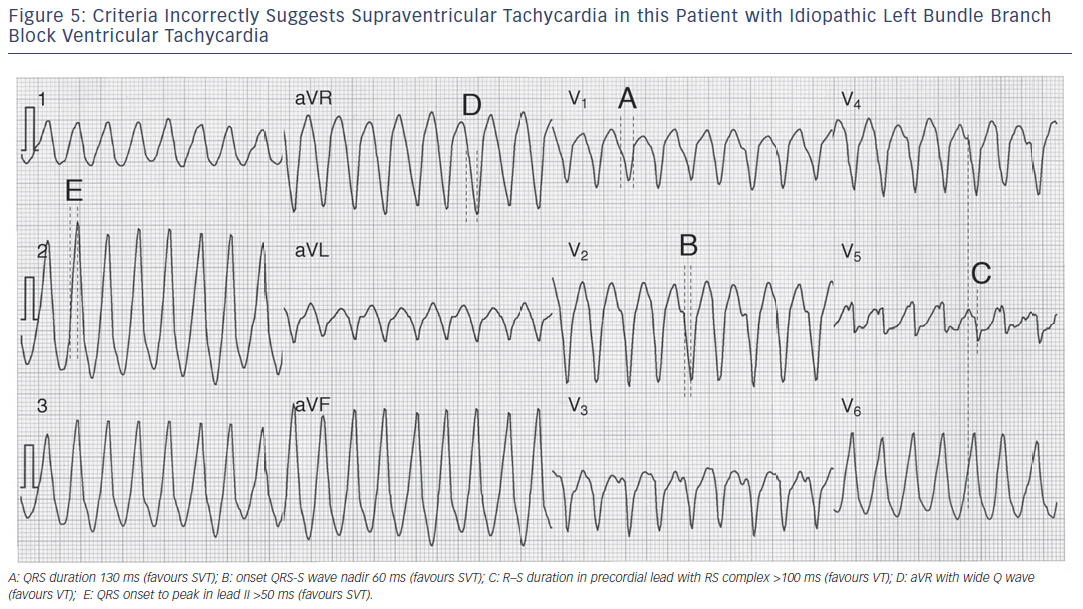



Wide Complex Tachycardia Ventricular Tachycardia Or Not Ventricular Tachycardia That Remains The Question Aer Journal
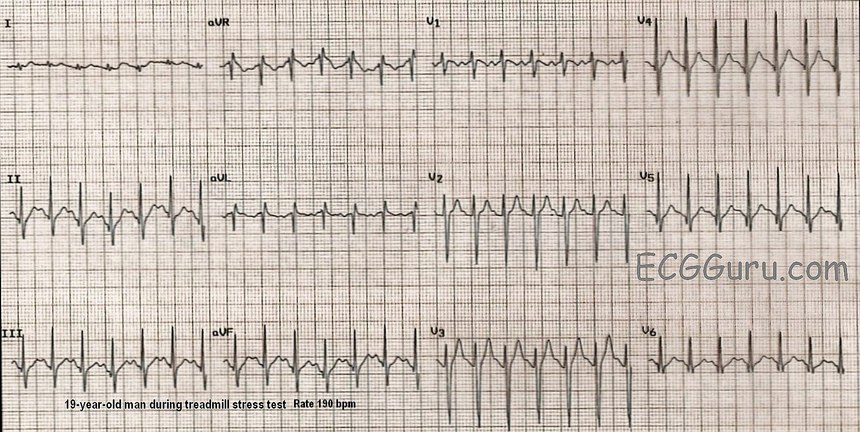



Sinus Tach Or Svt 4 Clues To Tell The Difference
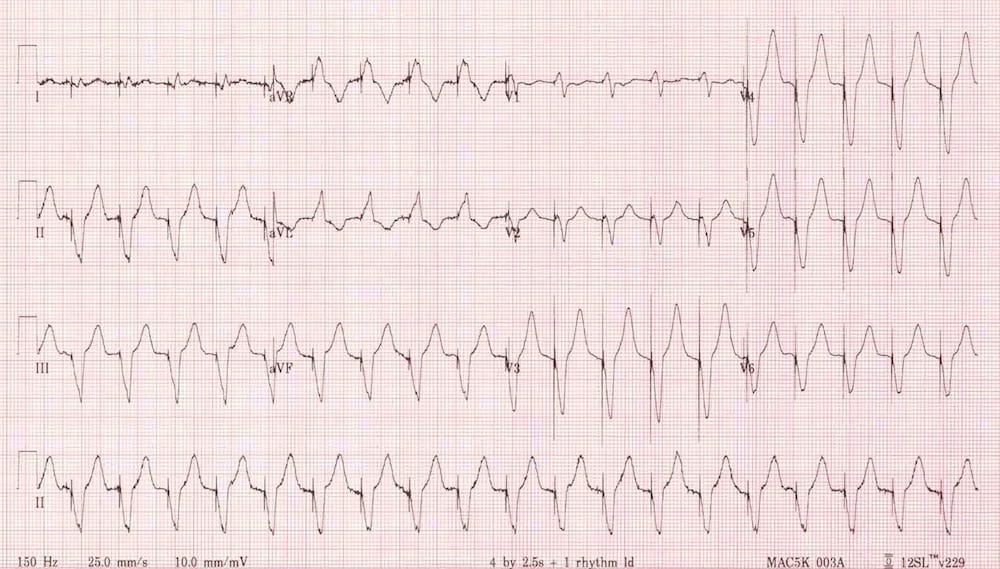



Vt Versus Svt Litfl Medical Blog Ecg Library Basics




Altered Heart Rhythm Nurse Key
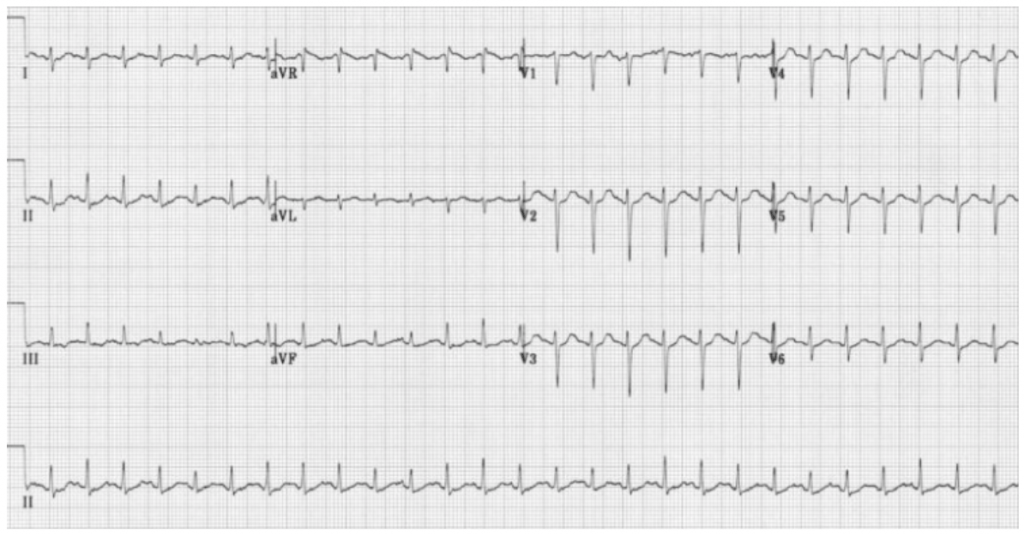



About Sinus Tachycardia Hope For Hearts Australia
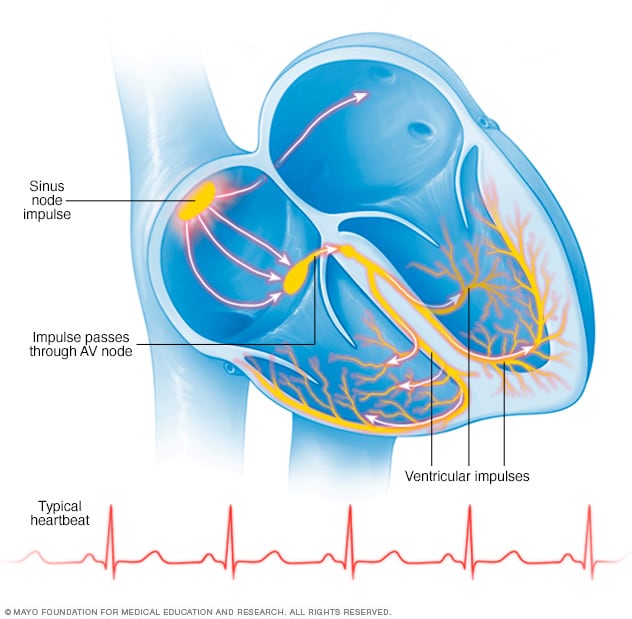



Ventricular Tachycardia Symptoms And Causes Mayo Clinic




Safety And Outcomes Of Ventricular Tachycardia Substrate Ablation During Sinus Rhythm A Prospective Multicenter Registry Sciencedirect



Mcgill Ekg Learning Project




Atrial Tachycardia Diagnosis And Treatment The Cardiology Advisor
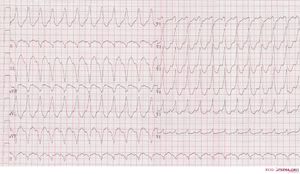



Ventricular Tachycardia Ecgpedia
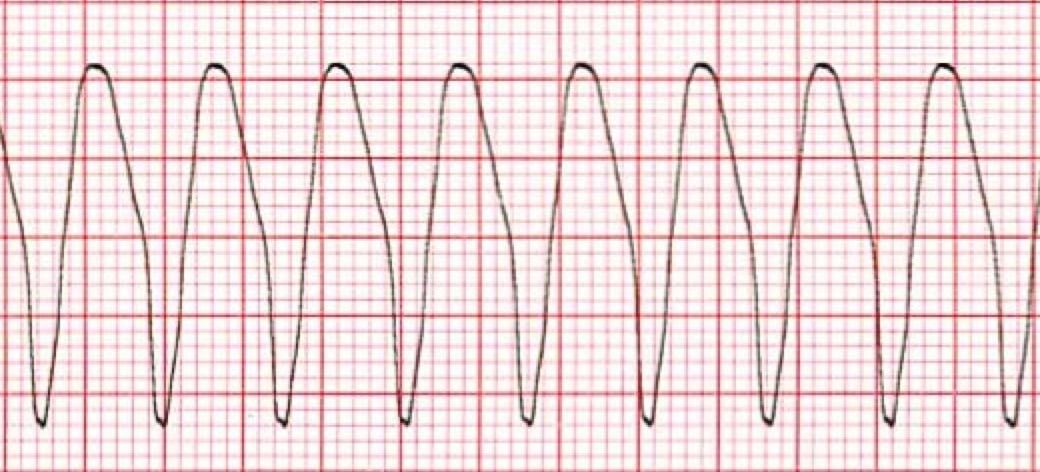



Wide Complex Tachycardia Training Acls Cardiac Rhythms Video Proacls



The Trouble With Sinus Tachycardia Ems 12 Lead




An Illustrative Description Of Different Arrhythmias Thaler 15 A Download Scientific Diagram




Polymorphic Ventricular Tachycardia An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
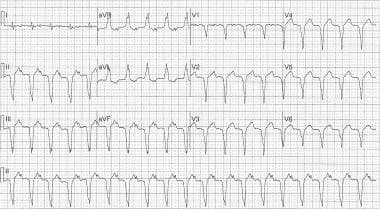



Y4eg751jjwv6bm



Supraventricular Tachycardia Wikipedia




Vt Versus Svt Litfl Medical Blog Ecg Library Basics




Pin On Nursing




Management Of Tachycardia Amboss




Cardiovascular Medicine Wide Complex Tachycardia
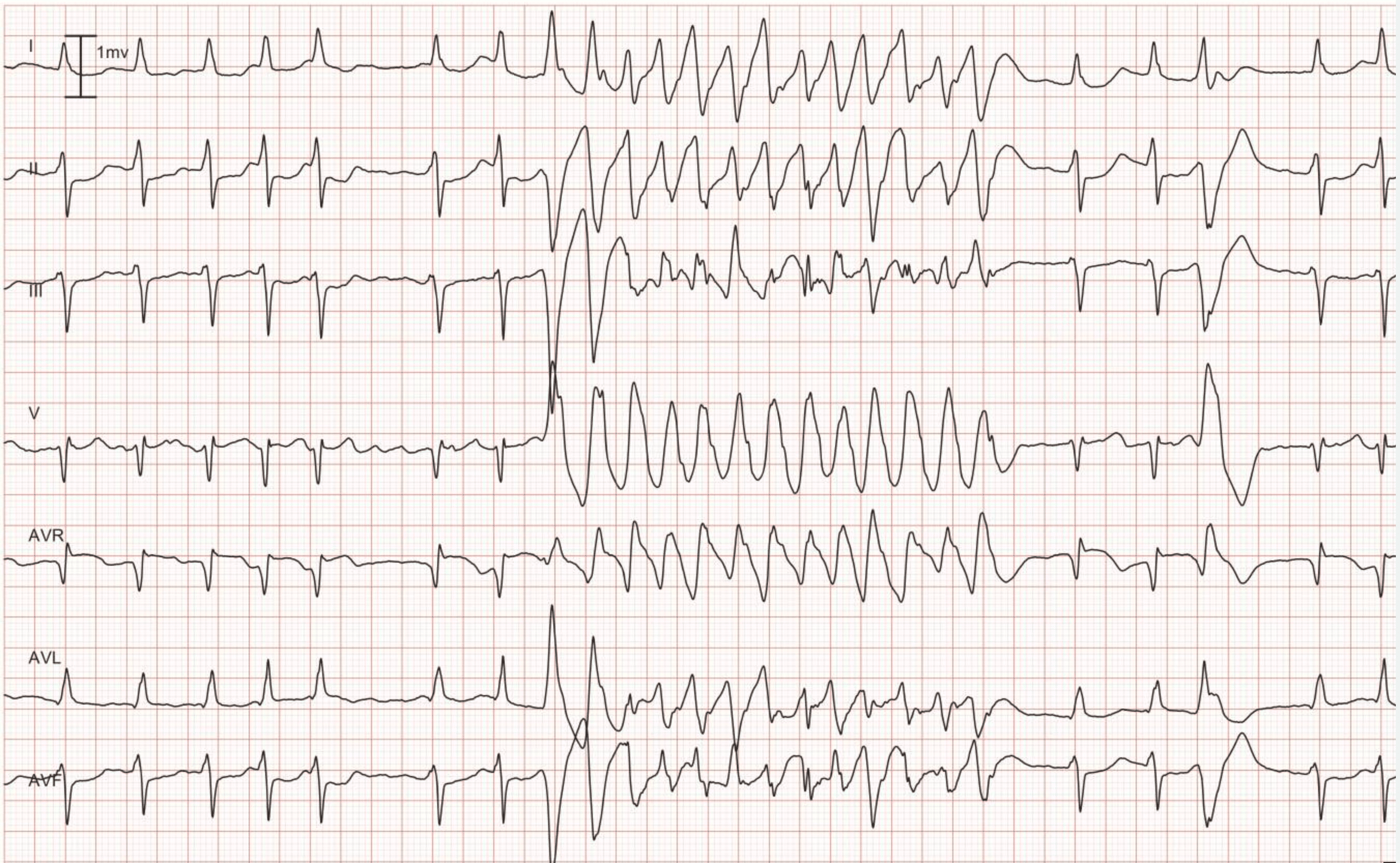



Ventricular Tachycardia Vt Ecg Criteria Causes Classification Treatment Management Ecg Echo




Sinus Tachycardia Images Stock Photos Vectors Shutterstock



1




Sinus Tachycardia Images Stock Photos Vectors Shutterstock



Em Cases Ecg Cases 19 Tachycardias




Overview Of Cardiac Arrhythmias Amboss
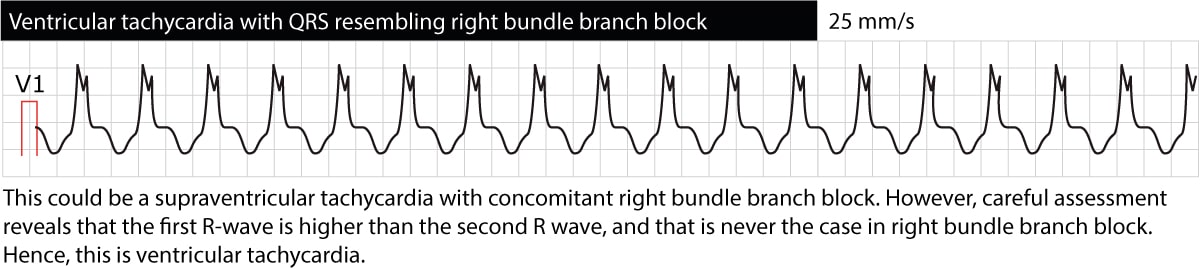



Ventricular Tachycardia Vt Ecg Criteria Causes Classification Treatment Management Ecg Echo




Ventricular Tachycardia With No Structural Heart Disease Recognition And Treatment The Cardiology Advisor
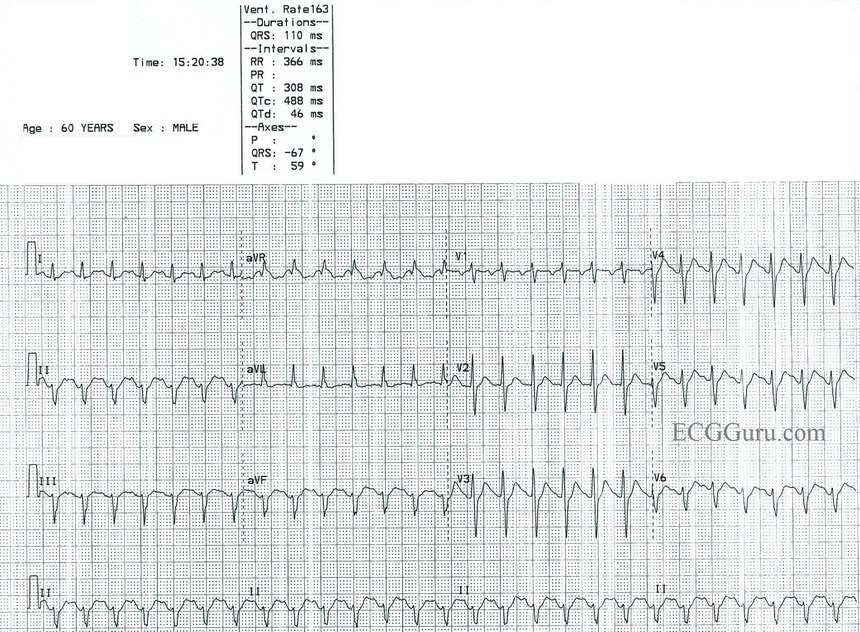



Sinus Tach Or Svt 4 Clues To Tell The Difference



The Trouble With Sinus Tachycardia Ems 12 Lead




Supra Ventricular Tachycardia Rythms Rythms Categorised As Supra Ventricular Tachycardia Svt Supra Ventricular Tachycardia Cardiology Teaching Package Practice Learning Division Of Nursing The University Of Nottingham
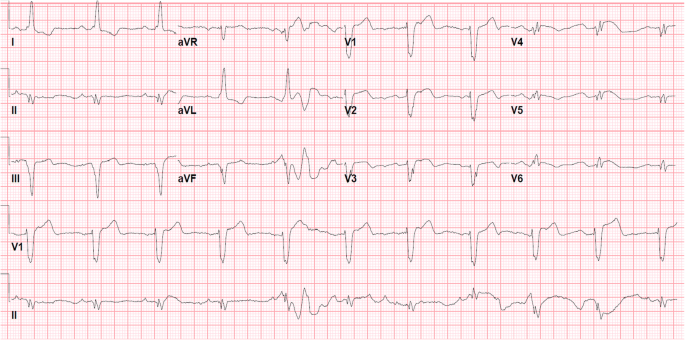



Bundle Branch Reentrant Ventricular Tachycardia Review And Case Presentation Springerlink




Em Cases Ecg Cases 19 Tachycardias
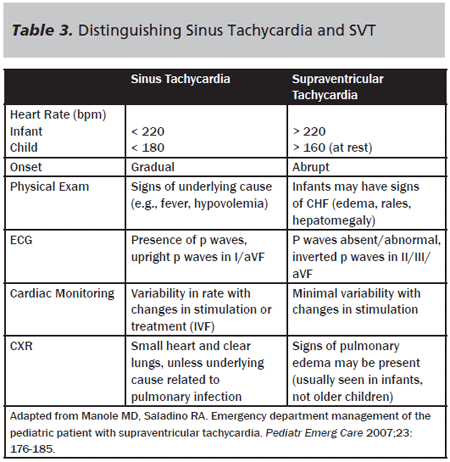



Supraventricular Tachycardia Vs Sinus Tachycardia Epomedicine
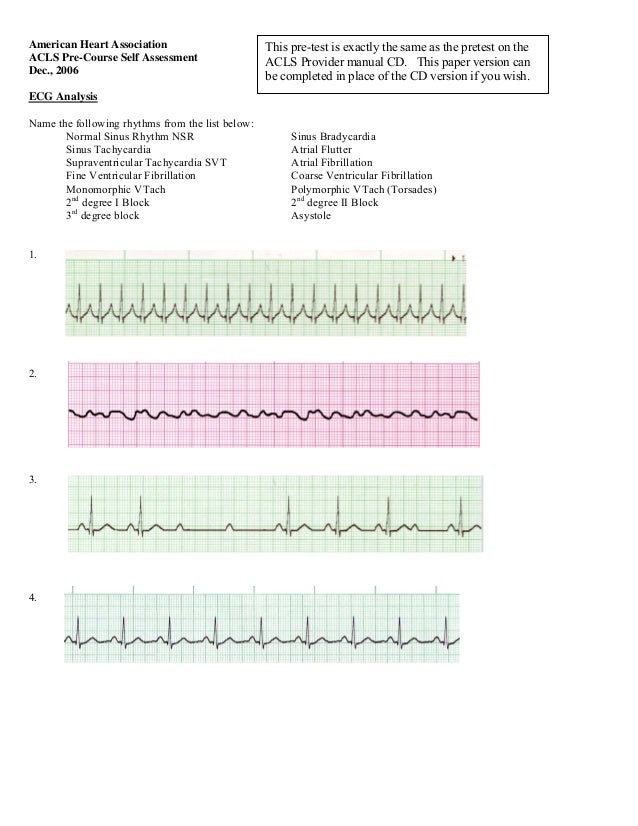



Ecg For Acls
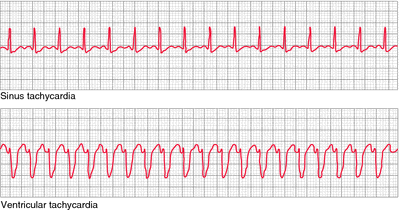



Sinus Tachycardia Definition Of Sinus Tachycardia By Medical Dictionary




Tachycardia Causes Signs Symptoms Types Diagnosis Treatment




Electrocardiographic Monitoring Various Rhythms And Dysrhythmias Ventricular Fibrillation Ventricular Tachycardia Atrial Fibrillation Atrial Flutter Supraventricular Ppt Download


コメント
コメントを投稿